List of Regular and Irregular Nouns and their Plurals
English is a fascinating and complex language, and one of the most interesting aspects of it is the way we form plurals.
The history of the English language, its etymology, and the various influences that have shaped it over time all play a role in the way we form plurals today.
In these ‘plural of’ blog posts, we'll delve into the history of the English language, explore the etymology of nouns, and discuss the most common rules for forming plurals in English.
The English language has its roots in the Germanic languages spoken by the tribes that migrated to the British Isles in the 5th century AD.
Over time, it has undergone several changes, including the influence of other languages such as Latin, French, and Greek. These influences have led to a complex system for forming plurals in English.

The etymology of nouns is also an important factor in understanding plurals.
Nouns can be divided into several categories based on their origins, including Germanic, Latin, and Greek nouns. Germanic nouns, for example, often form plurals by adding an -s or -es, while Latin and Greek nouns often change the ending of the word to indicate plurality.
One of the most common rules for forming plurals in English is adding -s to the end of a noun. This rule applies to most nouns that are not already in the plural form. For example, "book" becomes "books", "dog" becomes "dogs", and "cat" becomes "cats".
However, there are a few exceptions to this rule. For example, nouns ending in -s, -x, -z, -sh, or -ch usually form plurals by adding -es. This can be seen in words like "bus" becoming "buses", "box" becoming "boxes", "quiz" becoming "quizzes", "dish" becoming "dishes" and "church" becoming "churches".
Read our full blog post on how to form plurals in English.

Another common rule is nouns that end in -y. Here, if the noun ends in a vowel + -y, the plural is formed by adding -s.
For example, "boy" becomes "boys". However, if the noun ends in a consonant + -y, the plural is formed by changing the -y to -ies. For example, "city" becomes "cities".
There are also nouns that don't follow any of these rules and have irregular plurals. Some examples include "man" becoming "men", "woman" becoming "women", "foot" becoming "feet", "tooth" becoming "teeth" and "mouse" becoming "mice".
In addition to these rules and exceptions, there are also nouns that don't change in the plural form at all, such as "moose", "deer" and "sheep".
Read here for how to form plural possessive nouns.

In conclusion, understanding the history and etymology of the English language, as well as the most common rules for forming plurals, can help us better understand and use this complex language.
While the rules for forming plurals in English can seem daunting at first, with practice and an understanding of the various influences and exceptions, it becomes much easier to master.
Read about the difference between countable and uncountable nouns.
List of Plurals in English
What's the plural of crisis?

What's the plural of moose?

What's the plural of octopus?

What's the plural of axis?

What's the plural of analysis?

What's the plural of diagnosis?

What's the plural of fish?

What's the plural of roof?

What's the plural of basis?

What's the plural of bus?

What's the plural of deer?

What's the plural of fox?

What's the plural of index?

What's the plural of leaf?

What's the plural of curriculum?

What's the plural of cactus?

What's the plural of hero?

What's the plural of ox?

What's the plural of no?

What's the plural of platypus?

What's the plural of radius?

What's the plural of syllabus?

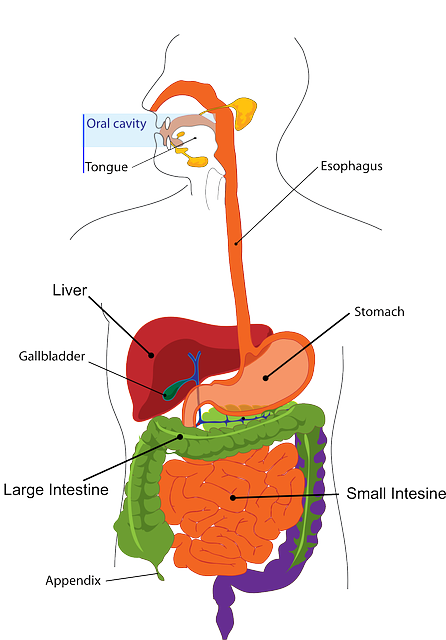
What's the plural of appendix?
What's the plural of die?

What's the plural of goose?

What's the plural of mongoose?

What's the plural of sheep?

What's the plural of alumnus?

What's the plural of alumna?

What's the plural of penis?

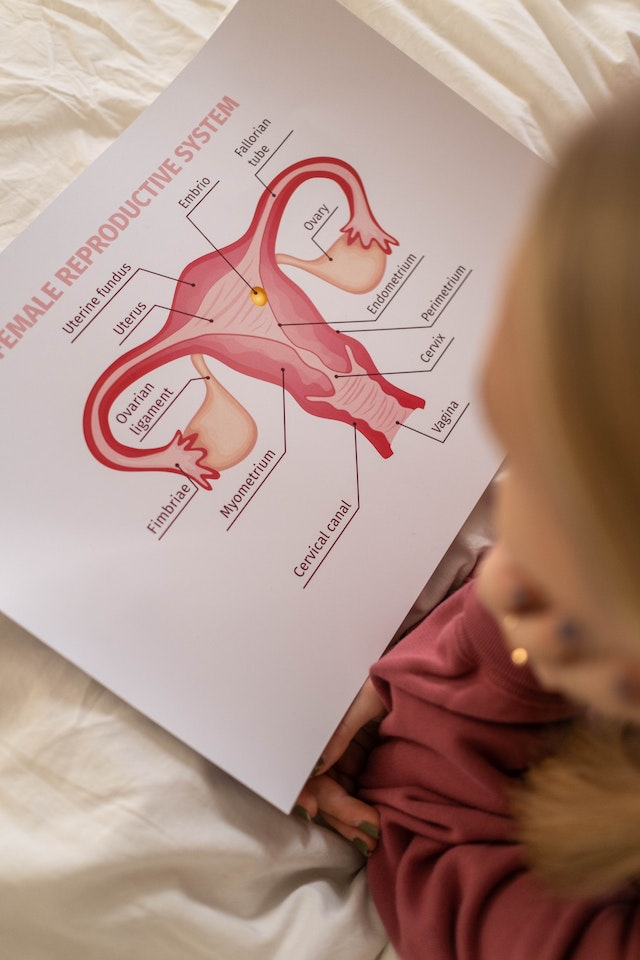
What's the plural of uterus?
What's the plural of apparatus?

What's the plural of calf?

What's the plural of Christmas?

What's the plural of criterion?

What's the plural of focus?

What's the plural of genus?

What's the plural of hippopotamus?

What's the plural of hypothesis?
What's the plural of matrix?
What's the plural of tomato?

What's the plural of antenna?

What's the plural of phenomenon?

What's the plural of quiz?

What's the plural of fly?

What's the plural of formula?

What's the plural of life?

What's the plural of man?

What's the plural of synopsis?

What's the plural of potato?

What's the plural of mouse?

What's the plural of mango?

What's the plural of attorney?

What's the plural of woman?

What's the plural of loaf?

What's the plural of memorandum?

What's the plural of oasis?

What's the plural of shrimp?

What's the plural of abacus?

What's the plural of buffalo?

What's the plural of monkey?

What's the plural of journey?

What's the plural of turkey?

What's the plural of knife?

What's the plural of elf?

What's the plural of forum?

What's the plural of aircraft?

What's the plural of half?

What's the plural of hoof?

What's the plural of medium?

What's the plural of thief?

What's the plural of donkey?

What's the plural of church?

What's the plural of valley?

What's the plural of vertex?

What's the plural of mosquito?

What's the plural of ostrich?

What's the plural of son-in-law?

What's the plural of story?

What's the plural of spy?

What's the plural of masseuse?
What's the plural of sir?

What's the plural of flamingo?
What's the plural of glass?

What's the plural of key?

What's the plural of safe?

What's the plural of zoo?

What's the plural of thesaurus?

What's the plural of compass?

What's the plural of address?

What's the plural of rendezvous?

What's the plural of honey?

What's the plural of ally?

What's the plural of stratum?

What's the plural of house?

What's the plural of loss?

What's the plural of atlas?

What's the plural of haiku?

What's the plural of quail?

What's the plural of library?

What's the plural of county?

What's the plural of army?

What's the plural of kiss?

What's the plural of mass?

What's the plural of hair?

What's the plural of reef?

What's the plural of praying mantis?

What's the plural of grass?

What's the plural of lamb?

What's the plural of daddy?

What's the plural of mommy?

What's the plural of stadium?

What's the plural of butterfly?

What's the plural of helix?
What's the plural of larynx?

What's the plural of cow?

What's the plural of squash?

What's the plural of ibis?

What's the plural of codex?

What's the plural of offspring?

What's the plural of tuna?

What's the plural of wharf?

What's the plural of watch?

What's the plural of dress?

What's the plural of cargo?

What's the plural of stigma?

What's the plural of pizza?

What's the plural of daughter-in-law?

What's the plural of circus?

What's the plural of brush?

What's the plural of dictionary?

What's the plural of theory?

What's the plural of runner-up?

What's the plural of cliff?

What's the plural of lotus?

What's the plural of bench?

What's the plural of sandwich?

What's the plural of research?

What's the plural of photo?

What's the plural of cortex?
What's the plural of thank you?

What's the plural of mom?

What's the plural of trolley?

What's the plural of bush?

What's the plural of studio?

What's the plural of veto?

What's the plural of memo?

What's the plural of banjo?

What's the plural of lettuce?

What's the plural of body?

What's the plural of grouse?

What's the plural of phylum?

What's the plural of referendum?

What's the plural of student?

What's the plural of beach?

What's the plural of halo?

What's the plural of samurai?

What's the plural of kangaroo?

What's the plural of duck?

What's the plural of power of attorney?

What's the plural of mess?

What's the plural of tax?

What's the plural of kiwi?

What's the plural of amoeba?

What's the plural of moss?

What's the plural of nexus?

What's the plural of witch?

What's the plural of peach?

What's the plural of genie?

What's the plural of water?

What's the plural of chicken?

What's the plural of bronchus?
What's the plural of gulf?

What's the plural of metropolis?

What's the plural of menace?

What's the plural of stereo?

What's the plural of soprano?

What's the plural of quiche?

What's the plural of septum?

What's the plural of dog?

What's the plural of toy?

What's the plural of alley?

What's the plural of zebra?

What's the plural of human?

What's the plural of beau?

What's the plural of fez?

What's the plural of swine?

What's the plural of logo?

What's the plural of torpedo?

What's the plural of spacecraft?

What's the plural of police?

What's the plural of aquarium?

What's the plural of father-in-law?

What's the plural of mother-in-law?

What's the plural of encyclopedia?

What's the plural of terminus?

What's the plural of history?

What's the plural of society?

What's the plural of policy?

What's the plural of friend?

What's the plural of news?

What's the plural of fax?

What's the plural of motto?

What's the plural of match?

What's the plural of jury?

What's the plural of rice?

What's the plural of modulus?

What's the plural of stomach?

What's the plural of branch?

What's the plural of chef?

What's the plural of mine?

What's the plural of candy?

What's the plural of cloth?

What's the plural of ravioli?

What's the plural of diverticulum?
What's the plural of specimen?

What's the plural of proof?

What's the plural of patio?

What's the plural of meniscus?

What's the plural of atrium?

What's the plural of query?
What's the plural of swan?

What's the plural of symposium?

What's the plural of day?

What's the plural of birthday?

What's the plural of bunny?

What's the plural of deity?

What's the plural of crab?

What's the plural of cattle?

What's the plural of dolphin?

What's the plural of antithesis?

What's the plural of hobby?

What's the plural of fellow?

What's the plural of tsunami?

What's the plural of ninja?

What's the plural of abyss?

What's the plural of right of way?

What's the plural of nanny?

What's the plural of madam?

What's the plural of navy?

What's the plural of speech?

What's the plural of fairy?

What's the plural of mink?

What's the plural of play?

What's the plural of six?

What's the plural of cuff?

What's the plural of scenario?

What's the plural of menu?

What's the plural of metastasis?
What's the plural of avocado?

What's the plural of jersey?

What's the plural of suffix?

What's the plural of kidney?

What's the plural of therapy?

What's the plural of study?

What's the plural of Bloody Mary?

What's the plural of tray?

What's the plural of trophy?

What's the plural of ferry?

What's the plural of ruby?

What's the plural of goat?

What's the plural of forest?

What's the plural of boar?

What's the plural of bacillus?
What's the plural of bureau?

What's the plural of tableau?

What's the plural of viscus?
What's the plural of meatus?
What's the plural of igloo?

What's the plural of cod?

What's the plural of hoax?

What's the plural of arch?

What's the plural of success?

What's the plural of belly?

What's the plural of emu?

What's the plural of monsieur?

What's the plural of breach?

What's the plural of ranch?

What's the plural of bunch?

What's the plural of porch?

What's the plural of puppy?

What's the plural of ganglion?
What's the plural of military?

What's the plural of sheriff?

What's the plural of ratio?

What's the plural of video?

What's the plural of artist?

What's the plural of maximum?

What's the plural of cranium?
What's the plural of premium?

What's the plural of joy?

What's the plural of jockey?

What's the plural of wax?

What's the plural of reply?

What's the plural of crucifix?

What's the plural of shoe?

What's the plural of training?

What's the plural of facility?

What's the plural of diary?

What's the plural of rally?
What's the plural of battery?

What's the plural of dolly?

What's the plural of kitty?

What's the plural of bee?

What's the plural of dove?

What's the plural of theory?

What's the plural of child?

What's the plural of strawberry?

What's the plural of strategy?

What's the plural of sugar?

What's the plural of stretch?

What's the plural of strife?

What's the plural of strength?

What's the plural of street?

What's the plural of gymnastics?

What's the plural of straw?

What's the plural of hypothalamus?

What's the plural of approach?

What's the plural of broccoli?

What's the plural of graffito?

What's the plural of lady-in-waiting?

What's the plural of light-year?

What's the plural of brother-in-law?

What's the plural of sister-in-law?

What's the plural of queue?

What's the plural of check-in?

What's the plural of grown-up?

What's the plural of grocery?

What's the plural of cat?

What's the plural of book?

What's the plural of whale?
What's the plural of man-of-war?

What's the plural of apple?

What's the plural of orange?

What's the plural of berry?

What's the plural of cherry?

